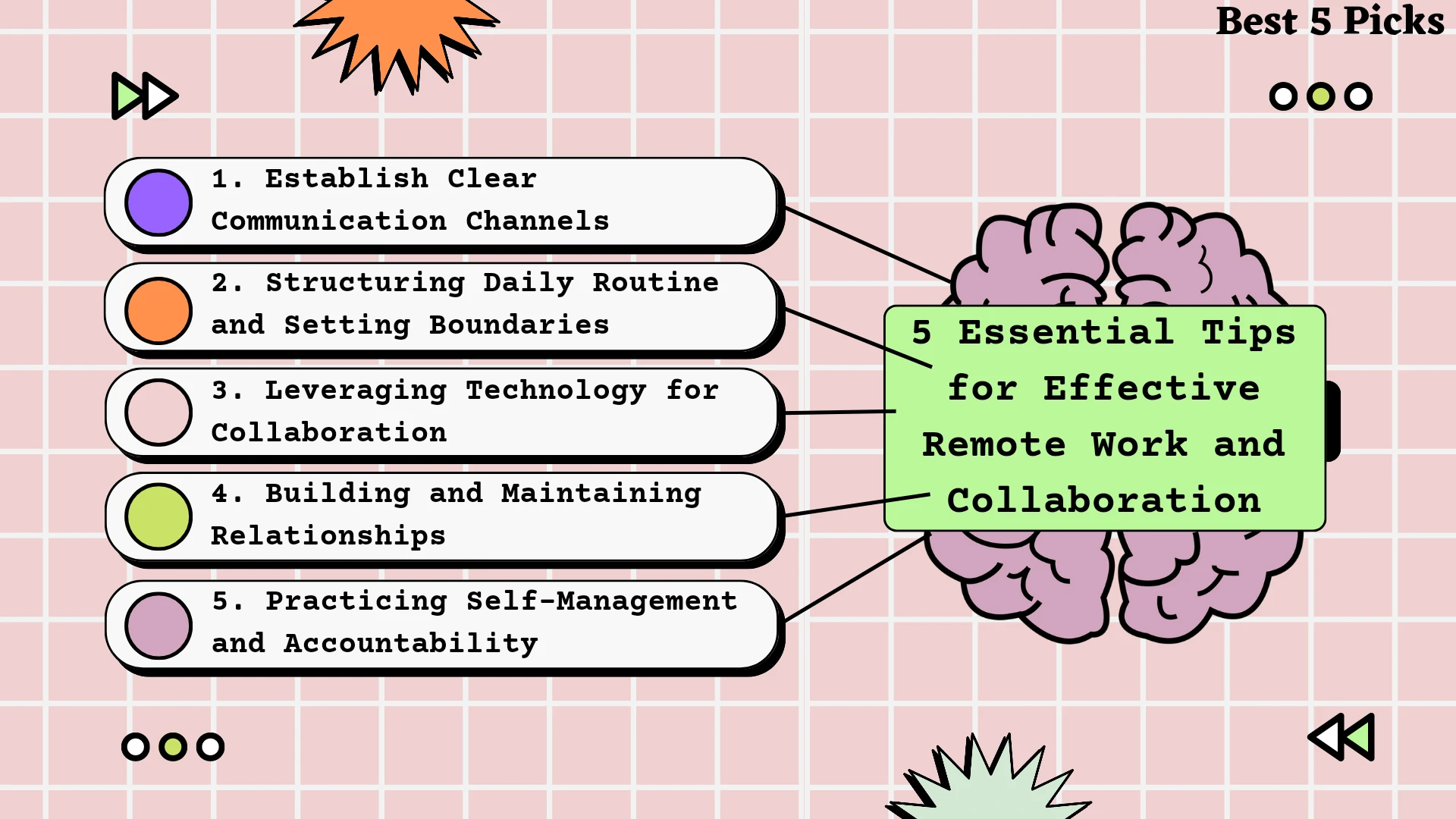
In today’s digital age, mastering key skills is vital for career success. Discover the top 5 skills for career success in the digital era.
From adeptness in data analysis to proficiency in coding, learn how these capabilities can propel your career forward.
Stay ahead of the curve by honing these essential skills and unlock a world of opportunities in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Gain a competitive edge by developing your expertise in areas such as digital marketing, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence.
Are You In Hurry? Then Check Out Below!
With the right skill set, you can navigate the complexities of the digital world with confidence.
Equip yourself with the tools necessary to excel in the modern workforce and position yourself for success in an increasingly digital-centric environment.
I. Introduction
Unleash Your Potential: Master These 5 Skills for Digital Career Success! Stay ahead in the digital era.
A. The rise of the digital era and its impact on careers
The world is changing dramatically as we enter the digital age. Technological advancements such as artificial intelligence, automation, big data and the internet have transformed the way we live and work.
The digital age has brought rapid and unprecedented change to businesses, creating both challenges and opportunities for entrepreneurs.
Traditional business functions are being transformed or even replaced by digital alternatives.
Companies are using technology to streamline operations, increase productivity and access global markets. As a result, individuals must adapt to this changing environment in order to succeed in their careers.
B. Importance of developing essential skills for career success
In this virtual era, having technical information by myself is not sufficient for profession fulfillment. Employers are searching for specialists who possess a broader set of competencies that permit them to navigate the virtual landscape efficaciously.
These critical skills go past technical information and are crucial for experts across industries.
Developing those competencies is essential for career achievement due to the fact they offer people with the capacity to stay relevant, agile, and adaptable in a unexpectedly changing paintings environment.
In the following sections, we can discover 5 essential abilties that specialists want to domesticate for career success within the virtual generation.
By growing these abilties, people can role themselves as treasured assets inside the digital body of workers and enhance their career possibilities.
II. 5 Skills for Career Success in the Digital Era
Discover the 5 skills you need to succeed in the digital era! This insightful article explores the key abilities that can propel your career to new heights.
From adaptability and flexibility to digital literacy, communication and collaboration, critical thinking and problem-solving, and continuous learning, we unveil the secrets to thriving in the digital world.
Stay ahead of the curve, enhance your professional growth, and embrace the opportunities that the digital era presents.
Read now for invaluable guidance on navigating the ever-evolving landscape of digital careers.
1. Adaptability and Flexibility

A. Embracing change and being open to new technologies
The technological and business environment is rapidly evolving in the digital age.
Thus, one of the essential skills for career success is the ability to embrace change and be open to new technologies. This skill set is an innovative mindset and a willingness to explore and adapt to emerging tools and platforms.
- Recognize the need for change:
Embracing change begins with understanding the needs of the context in a digitally driven world.
Entrepreneurs who recognize the benefits and opportunities that new technologies can offer are more likely to succeed in their careers. They understand that resisting change can lead to stagnation and hinder their potential growth.
- Willingness to learn:
Being open to new technologies requires a constant willingness to learn. This includes actively seeking knowledge on upcoming trends, attending training sessions and participating in professional development opportunities.
Employees who display a growth mindset and actively learn are better equipped to adapt to the ever-changing digital landscape.
- Agility to acquire new skills:
Adaptability also includes the ability to quickly acquire new skills as technology advances. These skills include identifying the skills necessary to thrive in the digital age and actively seeking opportunities for advancement.
Whether through online courses, workshops, or in-person courses, prioritize skill acquisition for individuals who can stay ahead of the curve and be competitive in their field.
- Other acceptances:
Embracing change means being open to innovation and experimentation. This requires actively exploring and exploring new technologies that can improve business processes and operations.
Employees who are willing to experiment with new tools and techniques demonstrate their ability to adapt and contribute to the growth and innovation of their organizations.
- Modification of roles and responsibilities:
Job roles and responsibilities are rapidly evolving in the digital age. Flexible and adaptable employees are likely to thrive in this environment.
They are willing to take on new challenges, change roles as needed, and adapt their skills to meet the changing requirements of the industry. These changes open up new opportunities for business growth and development.
B. Learning agility and willingness to acquire new skills
In the rapidly evolving digital age, flexibility and flexibility have become essential skills for career success. However, the key to adaptability is the ability to learn quickly and acquire new skills effectively.
This mini-thesis explores the concept of a learning pace and the importance of a willingness to continue to learn and grow.
- To understand learning speed:
Learning agility refers to an individual’s ability to learn from experience, adapt to new situations, and apply skills effectively.
This includes being open to new ideas, techniques, and technologies, and quickly understanding and applying new information.
Learning speed is not limited to specific technical skills but incorporates a broader concept of curiosity, adaptability and desire for self-improvement.
- Lifelong learning recognition:
Technology and services are constantly evolving in the digital age. Thus, a willingness to acquire new skills and a commitment to lifelong learning are essential to staying relevant and competitive in the workplace.
This means actively exploring learning opportunities through formal education, online courses, workshops, or even self-study. By embracing lifelong learning, individuals can better adapt to new roles, technologies, and industry practices.
- Developing a Growth Mindset:
A growth mind-set is the perception that one’s skills and intelligence can be advanced via willpower, attempt, and a willingness to research.
By cultivating a growth mindset, people come to be greater resilient, adaptable, and open to acquiring new competencies. They view demanding situations as possibilities for boom, instead of boundaries, and are more likely to persevere via setbacks.
This mind-set fuels a proactive approach to studying and enables people to embody new abilities and demanding situations with enthusiasm.
- Embracing Change and Uncertainty:
The virtual generation is characterized by means of speedy alternate and uncertainty. Technology improvements, marketplace shifts, and enterprise disruptions are common.
To thrive in such an surroundings, people want to develop adaptability and a willingness to include alternate. This includes being snug with uncertainty, being open to new ideas, and being proactive in seeking out possibilities to study and develop new capabilities.
- Seeking Diverse Learning Opportunities:
Learning agility is not restricted to formal education or traditional education applications. It includes seeking various studying possibilities and reviews.
This can include attending enterprise meetings, taking part in webinars, joining expert networks, or conducting mentorship applications.
By exposing oneself to a extensive variety of getting to know reviews, people can broaden their knowledge base, advantage different views, and enhance their adaptability.
C. Ability to adjust to evolving work environments and roles
In the digital age, workplaces and activities are constantly evolving due to technological advancements, changing market demands and global connectivity. To succeed in such a dynamic environment, businesses need a high degree of flexibility and flexibility.
This subtitle examines the importance of adapting to changing work environments and roles and provides strategies for developing this critical skill.
- Acceptance of changes:
a. Recognize the inevitability of change: Understand that change is constant in the digital age, and that resistance can hinder business growth.
b. Creating a growth mindset: Be positive about change and see it as an opportunity to learn and grow.
c. To build resilience: The ability to bounce back from setbacks and navigate uncertain and changing circumstances.
- Learning Agility:
a. Continuous learning: Embrace the concept of lifelong learning to stay up to date with the latest technology, trends and industry trends.
b. Embrace new technologies: Be open and adaptable to new digital tools, software and platforms that increase productivity and productivity.
c. Getting feedback: Actively seek feedback from colleagues, supervisors, and mentors to identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments.
- Modification of roles and responsibilities:
a. Apply to new roles: Be willing to accept new responsibilities and expand skill sets to meet the evolving needs of the organization.
b. Develop versatile skill sets: Develop skills that can be applied to different roles and functions, allowing for greater flexibility in career changes.
c. Cross-functional collaboration: Participate in projects or teams to access different areas of the project and increase flexibility.
- Agility in Remote Work Environments:
a. Virtual business skills: Develop effective communication and collaboration skills in remote work environments, such as video conferencing, online business management tools, and virtual team collaboration.
b. Time management and self-discipline: Stay productive and focused while working remotely with routines, goals, and resources distracting you from dealing with it.
c. Quality digital communication channels: Become proficient in a variety of digital communication channels such as email, instant messaging, and collaborative meetings, to drive effective and timely communication has been implemented.
- Embracing Innovation:
a. Embrace Emerging Technologies: Stay abreast of emerging technologies relevant to the industry and explore how they can be used to improve business processes and outcomes.
b. Experimentation and risk-taking: Foster a culture of experimentation and be willing to take calculated risks to adapt to changing market demands to drive innovation.
c. Agility in Problem Solving: Have a dynamic and creative problem-solving mindset that allows you to adapt quickly to complex and changing situations.
2. Digital Literacy

A. Understanding and utilizing digital tools and technologies
In today’s digital age, having strong digital literacy skills is critical to career success. Digital literacy refers to the ability to understand, analyze and effectively use digital tools and technologies.
This subtitle explores the importance of digital literacy in the workplace and provides insight into the specific skills required.
- Importance of Digital Literacy
a. Increased reliance on technology: With the rapid development of technology, businesses and organizations across sectors are increasingly relying on digital tools and platforms for their daily operation If these tools are understood and used used properly, can dramatically increase workplace productivity and efficiency.
b. Communication and collaboration: Digital literacy facilitates seamless communication and collaboration among team members, whether they are in the same office or working remotely.
It enables businesses to effectively use email, instant messaging, video conferencing, project management tools, and other digital channels to communicate and collaborate with colleagues, customers and stakeholders.
c. Access to information and resources: The digital age has transformed access and sharing of information.
Digital literacy empowers individuals to gather relevant information, conduct research, and explore online databases, search engines and shared knowledge to stay abreast of industry trends.
d. Career opportunities: Many emerging and high-growth industries require a strong foundation in digital literacy.
Digital marketing, data analytics, web development, UX design and other job functions look for those who can use digital tools and technologies to drive business results. Developing digital literacy skills opens up many career opportunities in a digital environment.
- Key Skills in Digital Literacy
a. Skills in business software: Digital literacy includes proficiency in widely used business software such as Microsoft Office Suite (Word, Excel, PowerPoint), Google Suite (Docs, Sheets, Slides), project management tools, collaboration types etc.
Professionals with a strong understanding of these tools can create, edit and share documents, analyze data, provide compelling information, and effectively collaborate on projects.
b. Familiarity with digital communication systems: Digital literacy includes the ability to navigate digital communication systems such as email clients, messaging applications, video conferencing tools (e.g., Zoom, Microsoft Teams), and capable virtual meeting platforms engage and collaborate with and implement colleagues and clients across locations.
c. Data analysis and interpretation: With so much data in the digital age, companies need to be comfortable working with data.
Digital literacy includes the ability to analyze and interpret data using tools such as spreadsheets, data visualization software, and statistical analysis programs.
These skills enable employees to make informed decisions, recognize patterns and trends, and derive actionable insights from data.
d. Cybersecurity skills: Digital literacy also includes knowledge of cybersecurity principles and best practices.
Employees need to understand the importance of protecting sensitive information, identifying potential risks, and conducting secure online transactions.
Be aware of cybersecurity risks and take reasonable precautions to ensure the security and integrity of digital assets and to enhance overall data security.
- Developing Digital Literacy Skills
a. Continuous learning: Digital tools and technologies are evolving rapidly. Employees should adopt a mindset of continuous learning and actively seek out opportunities to enhance their digital literacy skills.
This can be achieved through online courses, webinars, workshops and self-learning materials that focus on specific digital tools and technologies.
b. Assessment and practice: Hands-on experience is invaluable in developing digital literacy skills. Entrepreneurs need to explore digital tools and technologies, test their features and functionality, and apply them in real-world situations.
This helps build confidence and skills in using these tools effectively.
c. Peer learning and collaboration: Connecting with peers and colleagues who have strong digital literacy skills can be beneficial. Knowledge sharing and collaboration in projects requiring digital tools and technologies can create a collaborative learning environment.
Employees can exchange best practices, share tips and strategies, and tackle challenges together to improve their digital literacy skills.
B. Proficiency in using productivity software and online platforms
In today’s digital age, developing skills in the use of business software and online platforms is critical to career success.
The ability to use these tools effectively not only increases productivity but also allows individuals to adapt to a changing work environment.
Here we explore the importance of developing skills in business software and online platforms and discuss how they can contribute to business growth.
- Advanced Manufacturing:
Knowledge of management tools such as Microsoft Office Suite (Word, Excel, PowerPoint), Google Workspace, Trello or Asana, and collaboration teams such as Slack or Microsoft Teams, allows individuals to better manage their work, streamlining collaboration and improves overall efficiency.
By mastering these tools, employees can create and edit documents, analyze data, create presentations, collaborate, collaborate with team members, and manage tasks more effectively.
- Improved communication and collaboration:
Websites and communication tools have changed the way teams collaborate, especially in remote work environments.
Familiarity with tools such as video conferencing platforms (Zoom, Microsoft Teams, Google Meet) and instant messaging applications (Slack, Microsoft Teams, Discord) enable individuals to communicate seamlessly with team members, regardless of their physical location
So these skills remote collaboration, teamwork , . and strengthens employee relationships.
- Data analysis and interpretation:
Many businesses today rely heavily on data-driven decision making. Proficiency in data analytics tools and techniques such as Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, and Tableau enables businesses to effectively gather, analyze and interpret data.
These skills enable informed, trend-sensitive decision-making , models and insights, and help set data- driven strategies in their organizations.
- Adaptability to changing work environments:
The digital age brings with it constant changes in facilities and equipment. Knowledge development in automation software and online platforms allows employees to adapt quickly to these changes.
Whether it’s learning a new project management tool, collaborating on a cloud-based platform, or embracing emerging technologies, individuals with strong digital literacy skills can navigate this transition more effectively and they have remained at a high level.
- Continuing Professional Development:
Optimization software and online platform efficiencies are beneficial not only for current job functions, but also for business development.
Employers typically look for candidates who have a solid foundation in digital literacy skills, while demonstrating the ability to adapt, learn, and contribute effectively to the digital workplace.
By passing on their skills high in these tools on a consistent basis, employees can position themselves as valuable and competitive assets in the job market.
C. Familiarity with data analysis and interpretation
- Understanding data analysis:
a. Definition and Scope: Data analysis refers to the process of exploring, organizing, manipulating, and modeling data in order to discover meaningful patterns. It uses statistical techniques, algorithms, and visualization tools to extract valuable information from raw data.
b. Importance in decision making: Data analysis enables managers to make data-driven decisions. Data analysis allows individuals to identify trends, identify relationships, and make predictions, contributing to more informed and effective decision-making.
- Key elements of data analysis:
a. Data Collection: Familiarity with the various methods of data collection, including surveys, experiments and observations, is important. Understanding how valid and reliable data is collected enhances the authenticity and validity of the research.
b. Data cleaning and cleaning: Raw data often contains errors, redundancies, or missing values. Staff need to know how to clean and pre-process data to ensure its quality and fitness for analysis.
c. Statistical techniques: Knowledge of the use of statistical techniques such as descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, regression analysis, and hypothesis testing enables professionals to draw meaningful insights and produce reliable conclusions.
d. Data Visualization: Effective data visualization techniques, such as charts, graphs, and dashboards help present complex information clearly and concisely. Visual data enhances understanding and simplifies decision-making.
- Interpretation of data:
a. Understanding context: Interpreting data goes beyond numerical and statistical analysis. This involves contextualizing data in the specific industry, domain, or problem at hand. Employees must be able to connect the dots and draw logical conclusions that align with organizational goals.
b. Identify trends and trends: Experienced interpreters can identify trends, patterns, and relationships in the data. This provides insight into customer behavior, market trends, inefficiencies, or other important aspects of the business.
c. Extracting actionable insights: The ultimate goal of data interpretation is to generate actionable insights that drive decision-making and improve business performance. Professionals who can extract actionable insights from data are in high demand in the digital age.
- Equipment and Technology:
a. Familiarity with data analysis tools: Proficiency with popular data analysis tools such as Excel, R, Python, or SQL is essential. These tools provide extensive data manipulation, analysis and visualization capabilities.
b. Understanding data analytics platforms: With the rise of advanced analytics platforms, companies should be familiar with platforms like Tableau, Power BI, Google Analytics etc. These tools provide interactive dashboards and advanced analytics functionality to better analyze and present data.
3. Communication and Collaboration

A. Effective written and verbal communication skills
Effective communication skills have become even more important for career success in the digital age.
The ability to express yourself clearly and concisely through both written and verbal means is essential in a variety of professional situations, whether collaborating with colleagues, dealing with clients communicate, or provide feedback to stakeholders.
Here we delve into the importance of honing your communication skills and offer advice on how to enhance your written and verbal communication abilities.
- Writing Communication Skills:
a. Clear and concise: Clear and concise writing is paramount in the digital age, where information overload abounds. Use simple, precise language to communicate your ideas, and make sure your message is easily understood.
b. Proper Grammar and Spelling: Pay close attention to grammar and spelling, as they play an important role in maintaining professionalism and confidence. Read your written communication carefully before sending it.
c. Tone and Tone: Change your style to suit your intended audience and purpose. Whether it’s a formal email, a motivational offer, or a friendly message, adjusting your voice and tone accordingly helps you communicate effectively.
d. Structure and Structure: Organize your written communication logically, using headings, bullets, and paragraphs to increase readability. Present your ideas in a coherent and organized manner to engage the reader.
- Verbal communication skills:
a. Active Listening: Effective oral communication begins with active listening. Listen to the speaker, make eye contact, and show genuine interest. To gain understanding, summarize and explain what you have heard.
b. Specificity and Accuracy: Speak clearly, pronounce your words and use appropriate movement. Avoid growling or speaking too fast. Make it a point to share your ideas to make the point more clear.
c. Nonverbal communication: Remember that nonverbal cues like body language, facial expressions and gestures play an important role in communication. Watch your non-verbal cues and pay attention to the cues of others when you speak.
d. Empathy and Emotional Intelligence: Develop empathy and emotional intelligence to understand the perspectives of others and respond appropriately. Pay attention to the feelings and reactions of others during verbal communication.
- Benefits of technology in communication:
a. Virtual Communication: With the rise of remote work and virtual meetings, it is important to adapt your communication skills to digital platforms. Familiarize yourself with video conferencing tools, chat applications, and email etiquette to effectively communicate in virtual environments.
b. Business Email Etiquette : Practice appropriate email etiquette by using clear subject lines, addressing recipients appropriately, and maintaining a professional tone. Keep emails short, and avoid using idioms or acronyms that the customer is unfamiliar with.
c. Collaboration tools: Embrace collaborative tools such as project management systems, shared documents, and communication channels to improve teamwork and facilitate communication with colleagues.
B. Ability to collaborate in virtual teams and remote work settings
- Recognition of technology:
a. Collaboration tools skills: Virtual teams rely on a variety of collaboration tools such as project management platforms, video conferencing software, instant messaging apps, and document sharing platforms to communicate, share information, and collaborate informally tough.
b. Video conferencing ethics: Video conferencing has become the dominant form of communication for remote work. Understanding videoconferencing etiquette, such as being punctual, maintaining professional attire, remaining silent, and actively engaging in conversation, is essential to ensuring effective collaboration in virtual.
- Clear and effective communication:
a. Written Communication: Written communication is preferred due to lack of face-to-face meetings in virtual teams. Clear and concise writing skills, including appropriate grammar, structure, and tone, are essential for accurate presentation of ideas, directions, and presentations.
b. Active Listening: Actively listening and responding to team members’ ideas, concerns, and questions is critical to building relationships and understanding. Listening, explaining, and asking clarifying questions shows active listening in a virtual team setting.
c. Cultural sensitivity: Virtual teams often have members from different cultures. It encourages inclusive collaboration through cultural sensitivity, respect for different perspectives, and adapting communication styles to different cultural values and practices.
- Creating and reporting the trust:
a. Setting clear expectations: Clearly defining roles, responsibilities, and objectives in a virtual collaboration at the beginning helps establish a foundation of trust. This helps everyone realize their contribution and value.
b. Regular and open communication: Regular check-ins, updates and feedback sessions are essential to maintain open communication in virtual teams. Resolving conflict early by encouraging open dialogue helps build trust and cooperation.
c. Virtual Team Building Activities: Virtual team building activities, such as icebreaker exercises, virtual social events, and shared interest groups, help foster a sense of camaraderie and strengthen team relationships despite physical distance.
- Terms of Use and Responsibility:
a. Realistic deadlines: Establishing realistic deadlines for tasks and projects is essential to ensuring efficiency in virtual teams and avoiding misunderstandings Clearly communicating timelines and milestones helps everyone keep him on the road, and take good care of his work.
b. Self-discipline and agility: Remote work requires individuals to be self-motivated, disciplined, and proactive. Being proactive, meeting deadlines, and being accountable for your work helps create a productive and collaborative virtual team environment.
a. Quick conflict resolution: Conflicts can arise in virtual teams due to miscommunication, differences of opinion, or misunderstandings. Resolving conflicts quickly, clearly and respectfully is essential to preventing further problems and maintaining good working relationships.
b. Practical Problem Solving: Encourages cooperation by encouraging team members to engage in proactive problem solving when conflict arises and helps find practical solutions. This may include dialogue mediation, search validation, or other avenues of evaluation.
C. Strong interpersonal skills for building professional relationships
Active listening: Active listening is key to effective interpersonal communication. It involves full communication, understanding, and empathy.
Active listening is even more important in digital systems where face-to-face communication can be restricted.
Active listening leads to a better understanding of others’ perspectives, concerns, and actions, and establishes cooperation and positive trust.
Clear and concise communication: In the digital age, communication is often done through written channels such as email, instant messaging, or video conferencing.
Being able to express yourself clearly and concisely is essential to conveying the message accurately and avoiding misuse.
Using appropriate grammar, structuring messages, and adapting to different platforms and audiences are all important parts of clear and concise communication.
Virtual Collaboration: Collaborating effectively in virtual teams requires strong interpersonal skills.
This includes being able to work in harmony with colleagues from different backgrounds and cultures despite being physically isolated. Effective virtual collaboration requires active engagement, sharing ideas, providing constructive feedback, and respectfully resolving conflict.
Building relationships with team members through authentic communication is critical to creating a positive and productive work environment.
Emotional Intelligence: Emotional intelligence refers to the ability to understand and manage one’s own and others’ emotions.
It plays an important role in human relationships, especially in the digital age when non-verbal cues may be limited or non-existent.
Developing emotional intelligence will enable you to navigate conflicts, handle difficult conversations, show empathy and support to colleagues, and ultimately build trust and strong relationships.
Building connections and relationships: Building professional connections is critical to business success in the digital age.
Strong interpersonal skills keep you in touch with industry colleagues, mentors and potential employers.
Actively participating in online communities, attending virtual conferences, and using social media platforms can help expand your network and create opportunities for collaboration and career growth.
Conflict Resolution: Conflicts can arise in any business environment. With strong interpersonal skills, you can manage conflicts constructively and find practical solutions.
Active listening, effective communication, and empathy play an important role in resolving conflict and maintaining good working relationships.
4. Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving

A. Analytical skills to evaluate complex situations and information
In the digital age, individuals with strong analytical skills have a huge career advantage. With so much information and information available, the ability to critically assess complex situations and make informed decisions is essential.
Here we delve into the importance of analytical skills and how they contribute to business success in the digital age.
- Data analysis:
Analytical skills include the ability to collect, interpret, and analyze data for meaningful insights. Proficiency in data analytics allows employees to identify trends, patterns, and relationships, enabling them to make evidence-based decisions.
In today’s data-driven world, individuals who can use data analytics tools and techniques have a competitive advantage.
- Problem Identification and Definition:
Strong analysts have the ability to identify problems and define them accurately. Complex issues can be broken down into manageable parts, making it easier to clearly understand the challenges at hand.
This skill is especially valuable in the digital age, where new problems often arise from technological advances and changing market dynamics.
- Reasonable assumptions:
Analytical skills require the use of logical reasoning to assess situations and draw conclusions. Employees with this skill can objectively weigh multiple perspectives and weigh a variety of factors before making a decision.
Logical reasoning is essential in problem solving situations where critical decisions must be made quickly and effectively.
- Analysis of alternatives:
In complex situations, thinkers excel at exploring possible options and calculating possible consequences. They can weigh the pros and cons, determine the risks and benefits, and make appropriate choices.
These skills are especially important in the digital workplace, where individuals are often faced with multiple solutions or technology options.
- Alternative problem solving:
Thinkers have a knack for creative problem solving. They can think outside the box and come up with creative solutions to challenges.
In the digital age, where technology is advancing rapidly, companies must find new ways to solve emerging problems. Analytical skills enable individuals to be flexible and think creatively in the face of uncertainty.
- Attention to detail:
Attention to detail is an important part of analytical thinking. Employees with strong analytical skills pay close attention to detail, ensuring accuracy and thoroughness in their analysis.
They can identify inconsistencies or similarities that can affect decision-making processes. In the digital age, where data integrity is critical, this skill is extremely useful.
- Continuous Improvement:
Analytical thinkers have a growth mindset. They constantly seek answers, reflect on their decisions, and refine their research methods.
This commitment to self-improvement develops employees to stay ahead of their careers, adapt to new challenges and take advantage of evolving technology.
B. Creative problem-solving abilities in digital contexts
In a digital age where technology continues to evolve and businesses increasingly rely on digital tools and platforms, the ability to think creatively and solve problems in a digital environment critical to business success Creative problem solving goes beyond traditional thinking and encourages innovative ways to overcome challenges and capitalize on opportunities.
Here are some key ingredients for creative problem solving in digital environments:
Embracing a growth mindset: A growth mindset is essential for developing creativity and problem-solving skills. It includes the belief that skills and abilities can be acquired through dedication and effort.
By adopting a growth mindset, individuals are more open to exploring new ideas, taking risks and thinking outside the box in the face of digital challenges.
Digital language development: Effective use of digital technologies and platforms is essential to successfully solve problems in a digital environment.
This includes understanding the capabilities and limitations of various digital tools, as well as an understanding of emerging technologies that can be used to find new solutions.
Applying the principles of reasoning: Reasoning is a problem-solving method that emphasizes empathy, experimentation, and iteration.
By applying systems thinking principles to digital environments, entrepreneurs can gain a deeper understanding of the user’s needs and pain points, and create more user-friendly solutions that address these issues use it properly.
Encourage collaboration and diversity of perspectives: Creative problem solving often benefits from collaboration and diversity of perspectives.
In a digital environment, this could be working in cross-functional teams, engaging with experts from different industries, or seeking input from users and stakeholders there If different perspectives are accepted, projects can offer a wide range of perspectives and possible solutions.
Benefits of data and analytics: Data plays a key role in solving problems, and the digital age provides access to a wealth of data that can inform decision-making.
Employees with creative problem solving capabilities understand how to collect, analyze and interpret information to gain insights and implement new solutions.
They are adept at using digital analytics tools to identify trends, patterns and opportunities that can lead to creative solutions.
Embrace experimentation and iteration: Creative problem solving in digital environments often involves experimentation and iteration. Employees must be willing to test hypotheses, gather feedback, and reiterate their solutions based on results.
This iterative process allows for continuous improvement and improvement in the digital solution, resulting in more effective problem solving.
Staying abreast of digital trends: The digital landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies, platforms and trends constantly popping up.
Employees with creative problem solving are continually exposed to these factors and adapt their problem solving strategies accordingly. They actively seek out learning opportunities, attend industry events, and engage with online communities in order to stay ahead of digital innovation.
C. Decision-making based on data and evidence
Understanding the role of data:
In the digital age, data is plentiful and accessible. However, the key remains to understand how to properly interpret these data.
Companies need to know data types that are relevant to their business, such as customer demographics, market trends, or performance statistics.
They need to understand the limitations and potential biases associated with data sources, and ensure that informed decisions are made appropriately.
Dimensions for Analysis:
Critical thinking is essential for evaluating data and gaining meaningful insights. Professionals must develop their analytical thinking abilities to identify patterns, relationships and trends in data.
It involves breaking down complex problems into smaller pieces, analyzing data, and drawing conclusions using logical reasoning.
Evidence-Based Decision Making:
Decision-making based on hard evidence rather than emotion or personal bias is a hallmark of a successful entrepreneur in the digital age.
By using data, individuals can objectively evaluate options and make appropriate choices.
They must be able to identify reliable sources of information, critically assess the quality and adequacy of the information provided, and use it as a basis for decision-making
Adoption of data-driven tools and technologies:
With the advent of advanced analytical tools and technologies, professionals have access to powerful tools that can help with data analysis and decision-making Individuals may be open to embracing these tools and technologies, such as data visualization software, predictive analytics models , machine learning algorithms to take advantage and make informed decisions .
Ongoing learning and change:
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and companies need to adapt their decision-making processes accordingly.
They need to stay abreast of emerging technologies and industry trends that affect data availability and interpretation.
Continuing education in online courses, workshops, or professional networking can enhance the ability to effectively analyze data and make informed decisions in dynamic environments.
Ethical considerations:
While data can provide valuable insights, employees should also consider ethical implications when making decisions.
This includes respecting data privacy and security, avoiding biased interpretation, and ensuring that decisions align with ethical guidelines and legal requirements Ethical decision-making in the digital age inspires trust , provides transparency, and drives sustainable business improvement.
5. Continuous Learning

A. Commitment to ongoing learning and self-improvement
A commitment to continuous learning and self-improvement is critical to business success in the fast-paced and ever-evolving digital age.
Technological advances, market trends, and industry trends are constantly evolving, making it imperative for companies to stay on the leading edge.
Embracing a growth mindset: Continuous learning begins with developing a growth mindset—the belief that power and wisdom can be achieved with dedication and hard work.
This mindset enables individuals to respond to challenges with flexibility, embrace feedback, and seek opportunities for continuous improvement.
Setting learning goals: Employees who are committed to continuous learning set clear learning goals that align with their career aspirations.
These goals may include developing new technologies, gaining domain expertise, or expanding knowledge in emerging areas. By setting specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, time-bound (SMART) goals, individuals can stay focused and motivated.
Explore learning opportunities: Continuing education extends beyond the traditional classroom setting.
Employees should actively seek out learning opportunities such as attending workshops, conferences and seminars, enrolling in online courses, attending webinars, and attending professional groups.
These channels uncover new ideas, industry best practices, and networking opportunities.
Adoption of online learning options: The digital age has brought with it a plethora of online learning options offering courses and materials on a wide range of topics.
Platforms like Coursera, edX, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning offer easy and convenient learning options.
Employees can use these workshops to develop new skills, earn certifications, and stay abreast of industry developments.
Building personalized learning networks: Connecting with like-minded professionals in your field can be invaluable for further education.
Actively participate in online communities, forums and social media groups to connect with industry experts, share knowledge, and learn from the experiences of others.
Creating a Personal Learning Network (PLN) fosters collaboration, allows you to connect with different perspectives, and opens doors to new opportunities.
Learning concepts and applications: Continuous learning is not just about acquiring knowledge; It also involves reflecting on what you have learned and applying it to real situations.
Take the time to see how your new skills or knowledge can be applied to your business. Practicing and actually applying what you have learned strengthens your understanding and enhances your problem-solving abilities.
Change and adaptation: The digital age is characterized by rapid change and disruption.
Employees who are committed to continuous learning understand the importance of embracing change and adapting to new technologies, tools and processes.
They are proactive in staying abreast of the latest trends and seek out opportunities for skill development or reskilling as needed.
B. Seeking out new knowledge and staying updated with industry trends
Embrace a growth mindset: Adopting a growth mindset is essential for ongoing learning. This view recognizes that power and wisdom can be acquired through effort and study. By adopting a growth mindset, individuals are likely to seek new knowledge and solve challenges.
Networks and professional circles: Connecting with business networks is a great way to get feedback on business trends. Attend conferences, workshops and webinars related to your area of interest. Connect with like-minded professionals on social media platforms or join online communities discussing industry trends.
Industry publications and newsletters: Subscribe to industry publications, newsletters and blogs that provide insights into the latest trends, developments and best practices in your industry. Reading these resources regularly will help you stay up to date with the latest developments and gain a deeper understanding of your industry.
Online learning platforms: Use online learning platforms such as Coursera, Udemy, LinkedIn Learning, or Khan Academy. This conference offers a wide range of classes and courses on a variety of topics including technology, data analytics, digital marketing, and more. By enrolling in related courses, you can gain new skills and expand your horizons.
Employee Development Programs: Many organizations offer professional development programs to their employees. These programs can include workshops, seminars, or training sessions aimed at developing specific skills or exposing employees to ongoing industry trends. Take advantage of these opportunities and learn from experts within your organization or industry.
Mentoring and coaching: Look for mentors or coaches who can guide you through your career journey. Mentors can provide valuable insight, advice, and guidance based on their own experiences. They can also help you identify learning opportunities and suggest resources to stay abreast of industry trends.
Podcasts and webinars: Podcasts and webinars are easy ways to consume knowledge on the go. Many industry experts and thought leaders produce podcasts or host webinars where they share insights, discuss trends, and offer valuable advice. Look for podcasts and webinars related to your field and listen during your commute or leisure time.
Cross-functional exposure: Look for opportunities to work on cross-functional projects or collaborate with colleagues from different departments. This book can help you expand your horizons, expose you to new ideas, and understand how different areas of your organization or industry are evolving.
C. Embracing online learning platforms and resources
One of the most important skills for business success in the fast-paced and ever-changing digital age is a commitment to continuous learning.
With technology advancing rapidly and industry constantly changing, the adoption of online learning methods and resources has become increasingly important.
Here we explore the benefits of embracing these platforms and resources and how they can boost your career prospects.
Access to a variety of study materials:
Online learning platforms offer a wide variety of courses, courses and resources across disciplines, allowing you to explore new areas of knowledge and gain valuable knowledge These platforms provide access to experts, industry professionals and thought leaders from around the world approach.
Whether you want to learn about digital marketing, data analytics, or graphic design, online platforms offer a wealth of resources to help you gain new skills.
Flexibility and convenience:
One of the main advantages of online learning is its flexibility and convenience. Unlike traditional education, online platforms allow you to learn at your own pace and on your own schedule.
This flexibility is especially beneficial for working professionals who may have little time to devote to classes. With online classes, you have the freedom to choose when and where you want to study, making it easier to balance your work and personal commitments while continuing to study.
Cost efficiency:
Online learning programs often offer inexpensive or even free courses, making education accessible to a wider audience.
Compared to traditional education which can be expensive due to tuition, textbooks and travel expenses, online learning offers a cost-effective alternative along with savings on travel and accommodation, because you can get learning from your home or office.
These costs allow individuals from a variety of socioeconomic backgrounds to continue their education and advance their careers.
Interactive Learning Experience:
Online learning programs strive to create interactive and engaging learning experiences.
Through multimedia presentations, discussion sessions, quizzes and activities, these sessions provide active participation and collaboration among students.
Many conferences also provide opportunities to network and network with peers and industry professionals, allowing you to expand your professional network and learn from the experiences of others.
This networking aspect enhances your understanding of the topic and it makes you more interactive with the content.
Acceptance and Certification:
Online learning platforms often offer certificates upon completion of the course or program, which can add value to your resume and demonstrate your commitment to continuing education.
These certifications demonstrate your commitment to staying abreast of industry trends and developing new skills.
Employers increasingly recognize the value of online learning and consider it a valuable asset when evaluating candidates for job opportunities or promotions By adopting online learning programs, you not only gain knowledge but you also increase your performance confidence.
Continuous learning is essential for career success in the digital age. Accepting online learning options and resources has access to a variety of learning materials, flexibility, costs, interactive learning experiences and recognition through certification.
If you use these options , enabling you to stay relevant, acquire new skills and adapt to the changing demands of the digital workforce. Embrace the opportunities offered by online learning and embark on a lifelong journey of continuous improvement and professional growth.
III. Conclusion
In this article, we have explored 5 Skills for Career Success in the Digital Era. Let’s recap these tips:
A. Emphasize the importance of developing and honing these skills
Developing and honing these critical skills is essential to career success in the digital age. As the digital landscape evolves, employees with these skills will gain a competitive advantage.
Employers value individuals who can adapt to change, use digital tools effectively, communicate and collaborate easily, think critically and solve problems, and continuously update their skills and knowledge.
By investing in these skills, employees can position themselves as valuable assets in their organizations and businesses. These skills enable individuals to stay relevant, meet complex challenges and seize opportunities in the digital age.
B. Encouragement to adapt to the changing landscape and thrive in digital careers
The digital age offers huge opportunities for business growth and success. But it also presents challenges that require individuals to be fast and nimble in their approach.
It’s important to embrace the changing landscape, be willing to learn and adapt, and constantly upgrade skills to thrive in a digital career.
By mastering the five essential skills outlined in this article, employees can unlock their full potential and succeed in the digital age.
Continuous learning, embracing technological advancements, effective communication, critical thinking and flexibility are the building blocks of a successful digital business
So, take charge of your career development, look for opportunities to develop these skills, and embrace the digital age with confidence. By doing so, you can set yourself up for long-term career success and stay relevant in an ever-evolving digital world.
IV. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Why is adaptability and flexibility so important in today’s digital age?
Adaptability and flexibility are crucial because technology and industries are constantly evolving. Being able to adjust to new situations, technologies, and methodologies ensures that you can thrive in dynamic work environments.
What does digital literacy entail, and why is it essential for career success?
Digital literacy involves having the skills to effectively use digital tools, platforms, and technologies. In the digital era, almost every aspect of work involves some form of technology, so being digitally literate is essential for tasks ranging from communication to data analysis.
How does communication and collaboration contribute to career success in the digital era?
Strong communication and collaboration skills are vital for working in distributed teams, remote environments, and across different cultures. Effective communication fosters teamwork, innovation, and the ability to convey ideas clearly amidst technological barriers.
Why are critical thinking and problem-solving skills emphasized in today’s digital workplace?
With the abundance of information available online, critical thinking is necessary to analyze data, evaluate sources, and make informed decisions. Likewise, problem-solving skills enable professionals to tackle complex issues and adapt solutions to fit changing circumstances.
How does continuous learning benefit individuals in the digital era?
Continuous learning is essential for staying updated with technological advancements, industry trends, and best practices. It allows professionals to remain competitive, adapt to changing job requirements, and pursue career growth opportunities.
Can adaptability be learned, or is it an innate trait?
While some people may have a natural inclination towards adaptability, it is a skill that can be developed through practice and experience. Embracing new challenges, seeking feedback, and being open to change are all ways to cultivate adaptability.
What are some practical ways to improve digital literacy?
Engaging in online courses, workshops, and tutorials can help individuals enhance their digital literacy. Additionally, regularly using digital tools and seeking out opportunities to learn new technologies on the job can further develop these skills.
How can one enhance communication skills in a digital work environment?
Actively participating in virtual meetings, utilizing collaboration tools effectively, and seeking feedback on written communication are ways to improve communication skills in a digital setting. Additionally, practicing active listening and being mindful of tone and context can aid in clear communication.
Are critical thinking skills only relevant for certain professions?
Critical thinking skills are valuable across various professions and industries. Whether analyzing data, problem-solving, or making strategic decisions, the ability to think critically is essential for success in almost any role in the digital era.
Is there a limit to how much one should focus on continuous learning?
Continuous learning should be viewed as a lifelong process rather than a finite goal. While it’s essential to prioritize learning based on career goals and industry demands, staying curious and adaptable to new knowledge and skills ensures continued growth and relevance in the digital era.
Disclaimer: This article, Best 5 Picks, is a sponsored piece provided by our partner. The recommendations and content shared here have been crafted in collaboration with the sponsor to provide value to our readers.